In the previous post we have seen the overview of ISSU types.
In this article, we will look at the detailed steps of the Compatible ISSU.
Detailed steps for Compatible ISSU
These are the steps for the compatible ISSU:
- Save configuration and check device
- Download software
- Check compatible version
- issu load
- issu run switchover
- issu accept
- issu commit
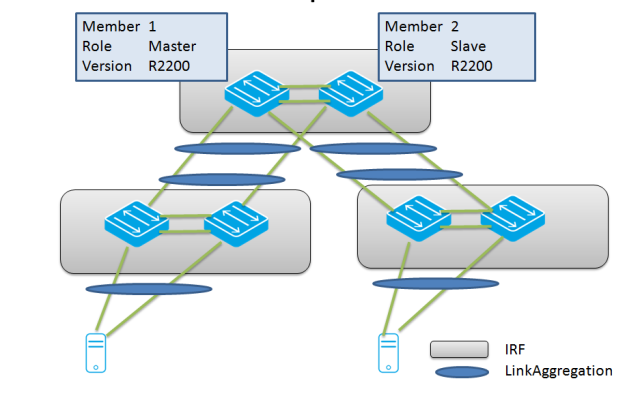
This is the sample base diagram for 2 core switches which will be updated from a version R2200 to R2200P02:
Save Configuration and check device
Verify all units are online and have the same current software versions.
In case of more than 2 units in the IRF, make sure unit 2 has the second best priority.
save display device display irf
Download software
Use ftp/tftp to get the new image on all units. Make sure you copy the file to each member local flash.
Check compatible version
Next verify the new version is compatible, this output is using fictive versions R2200P02 and R2200
display version comp-matrix file R2200P02.bin Number of Matrices in Table = 1 Matrix for A5xxx Running Version: R2200 Version Compatibility List: R2200P02(Compatible)
ISSU Load
In this step, a member device will be loaded with the new release R2200P02. The current master remains master with R2200. The member will join the IRF system again as member and synchronize the control plane (IRF) tables.
system-view issu load file RR2200P02.bin slot 2
- During the member 2 reboot, link-aggregation failover will ensure minimal (sub second) downtime:
- After member 2 has reloaded, the network is fully operational:
ISSU run switchover
This step will make the member 2 the new master of the IRF system. This is the moment the master role will operate using the new release. Handing over the master role is done a reboot of the current master.
issu run switchover slot 2
During the member 1 reboot, link-aggregation failover will ensure minimal (subsecond) downtime.
After member 1 has reloaded, the network is fully operational. Member 1 will join the existing IRF system as a slave (since an existing Master was found during the boot process.)
ISSU accept
Some people expect the old master to come online with the new version, however, this is not the case. It will simply come online with the existing software version, as a slave of the master unit 2.
The reason is to provide an easy way to perform a roll-back of the update.
Suppose the R2200P02 would cause some OSPF or STP problem on the network. The admin will need to install and run R2200 again on the system. Since the member 1 is now booted with the old R2200 as slave, it would be sufficient to reboot the member 2 (current R2200P02 master). This would cause the member 1 to become master again, running R2200. This step is known as the ISSU rollback.
There is an automatic rollback timer when you start the ISSU process, so it is important to “clear” the timer to prevent an unwanted automatic rollback. The ISSU Accept will stop the rollback timer.
issu accept slot 2
ISSU commit
After the accept, the member 2 is still running R2200P02. But it is the only device running the new version. In this step, the remaining units will be updated to the new release.
issu commit slot 1
This will reboot member 1 again, but this time it will come online with the new release.
Again, during the reboot, link-aggregation will ensure quick fail-over. Once the unit 1 has rebooted, the network is active/active online again:
Optional: revert master to unit 1
For an IRF system, the location of the master device is not important. But if you prefer to have it on unit 1 as a default, you will need to revert it, since the previous state left unit 2 as the master. This not part of the ISSU cli commands, so just a manual reload of unit 2.
reboot slot 2
During the reboot, link-aggregation failover will ensure minimal downtime.
Final situation
At this point the IRF system has been full updated.
Conclusion
Compatible ISSU provides minimal impact, mainly due to the fact that the control plane is fully sychronized between the memberes at each step. This means LACP, STP, ISIS states are 100% synced and this will minimize the failover time.
However, you have to be lucky to get this one, since it typically only applies to Pxx versions of the major release.










Pingback: Comware5 ISSU: Incompatible | About HP Networking
Pingback: Comware5 ISSU: Unkown (manual procedure) | About HP Networking
Well done. You should start doing documentation for HP.
Pingback: What will happen when the administrator attempts to use In-Service Software Upgrade (ISSU) for this upgrade? - Exam HP0-Y47 at ExamsDB
Release notes says compatible:
https://support.hpe.com/hpsc/doc/public/display?docId=a00050608en_us
Table 3 ISSU compatibility list
Current version Earlierversion Compatibility
5700-CMW710-R 2432P06 5700-CMW710-R 2432P05 Yes
Cli says not:
display version comp-matrix file ipe flash:/5700-CMW710-R2432P06.ipe
Verifying the file flash:/5700-CMW710-R2432P06.ipe on slot 2…………Done.
Boot image: 5700-cmw710-boot-r2432p06.bin
Version:
7.1.045
System image: 5700-cmw710-system-r2432p06.bin
Version:
7.1.045-Release 2432P06
Version compatibility list:
7.1.045-Feature 2426
7.1.045-Feature 2427
7.1.045-Feature 2428
7.1.045-Feature 2429
7.1.045-Feature 2430
7.1.045-Feature 2431
7.1.045-Release 2416
7.1.045-Release 2418P01
7.1.045-Release 2418P06
7.1.045-Release 2422
7.1.045-Release 2422P01
7.1.045-Release 2422P02
7.1.045-Release 2423
7.1.045-Release 2432P01
7.1.045-Release 2432P02
7.1.045-Release 2432P03
7.1.045-Release 2432P06
Version dependency boot list:
7.1.045
Slot Upgrade Way
1 Reboot
2 Reboot
Which one is right?
When in doubt, it is best to contact TAC to get more info..
They do not reply anything useful.
Well, no reply from HPE support at all, they replied, but nothing useful.
Performed upgrade as ISSU compatible on one of our IRFs.